Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage (PTBD)
What is percutaneous biliary drainage?
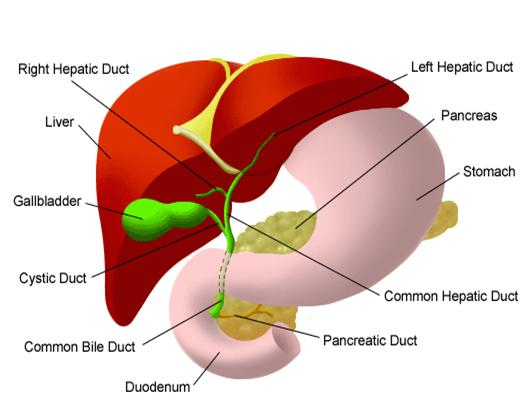

What is biliary stenting?
Sometimes the biliary drainage procedure may be extended with the placement of a permanent plastic or metal stent across the site of the bile duct blockage. Stents are usually inserted a few days after the initial drainage procedure and they keep the narrowed duct open without the need for a catheter.
Stenting may be preceded or followed by biliary dilatation, which involves dilating a segment of bile duct with a balloon to open up the stricture.
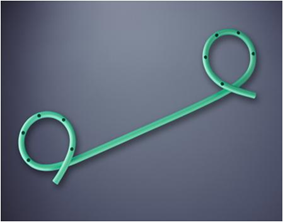
(A plastic biliar stent)
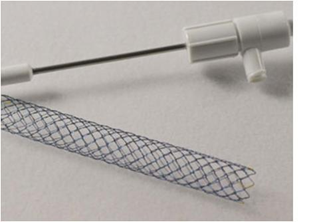
(A metal biliary stent)
What are the indications for percutaneous biliary drainage +/- stenting?
- Gallstones – in the gallbladder or within the bile ducts
- Inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis)
- Inflammation of the bile ducts (sclerosing cholangitis)
- Tumours of the pancreas, gallbladder, bile duct, liver
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the region of the pancreas and liver due to various types of tumours
- Injury to bile ducts during surgery
- Infection
Who will perform the procedure and where will it take place?
The procedure is performed by interventional radiologists. They are doctors specializing in minimally invasive treatments using image guidance. Interventional radiologists are trained to use diagnostic imaging equipment, such as x-ray and ultrasound, to guide various instruments during a procedure. The procedure will take place in the Interventional Radiology Department in a room especially adapted with x-ray and ultrasound equipment.
(A typical interventional radiology suite)
What are the risks of the procedure?
Although biliary drainage is a relatively safe technique, there are potential risks as with any procedure. Occasionally, it may not be possible to place the drain in the bile duct, in which case surgery may be required to relieve the blockage. Sometimes the bile may leak around the catheter and form a collection in the abdomen that can cause pain and may require drainage. Occasionally, the procedure can cause a blood infection (septicaemia) but prophylactic antibiotics are given to reduce this risk. Occasionally, bleeding may be a problem that requires a blood transfusion. Rarely, bleeding can be more severe and an embolisation procedure or surgical operation may be necessary.
With regards to biliary stents, they may be misplaced at the time of the procedure or may migrate following the procedure. These can be rectified by placement of a second stent in the correct place.

